Collagen is the most abundant form of protein found in the body, and makes up 25-35% of all protein in our bodies. It's one of the major building blocks of bones, skin, muscles, tendons and ligaments.
Collagen is also found in many other body parts, including blood vessels, corneas and teeth. It is the substance that holds the body together. Collagen forms a scaffold to provide strength and structure.
What is collagen?
Collagen is a hard, insoluble, and fibrous protein that makes up 25-35% of the protein in our bodies.
There are more than 16 types of collagen in our bodies1. The four main collagen types are I, II, III and IV. Type I, II, III Collagen accounts for 90% of your body's collagen.
Type II Collagen is made of more loosely packed fibers and is found in elastic cartilage, which cushions joints.
Type III Collagen supports the structure of muscles, organs and arteries.
Type IV Collagen helps with filtration and is found in layers of your skin.
In most types of collagen, the molecules are packed together to form long, thin fibrils. These act as supporting structures and anchor cells to each other. They give the skin strength and elasticity and provides structure to our skin, bones, tendons, fibrous cartilage, connective tissue and teeth.
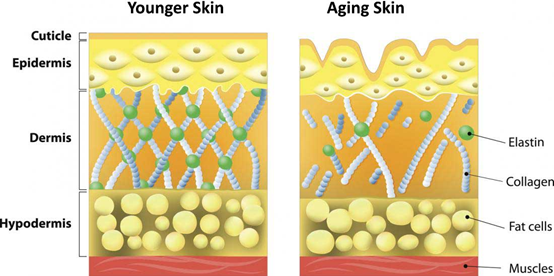
With age, our bodies produce less and lower-quality collagen. One of the visible signs of this is in your skin, which becomes less firm and supple thus more prone to wrinkles and fine lines. Some collagens act as protective coverings for delicate organs in the body, such as the kidneys.
In the dermis (the middle layer of skin), collagen helps form a fibrous network of cells called fibroblasts, upon which new cells can grow. Fibroblasts also plays a role in replacing and restoring dead skin cells.
With age, the body produces less collagen2. The structural integrity of the skin declines, wrinkles form, and joint cartilage weakens.
Women experience a dramatic reduction in collagen synthesis after menopause. After the age of 60, a considerable decline in collagen production is normal.
What Damages Collagen
When it comes to our health, prevention is much better than cure, so it's even more important to avoid the following collagen harming behaviours:
Eating sugar and refined carbs: Sugar interferes with collagen's ability to repair itself. Minimize your consumption of added sugar and refined carbohydrates3.
Smoking: Smoking reduces collagen production. Which can impair wound healing and lead to wrinkles4.
Too much sunshine: Ultraviolet radiation (UVA and UVB) can reduce collagen production. Avoid excessive sun exposure5.
Foods That Increase Collagen Production
All collagen starts off as procollagen. Our bodies make procollagen by combining two amino acids: glycine and proline. This process uses vitamin C.
Each Sunbio Collagen Peptides Beauty sachet contains 4875 mgs of Premium quality Australian derived Collagen Peptides, 100 mg of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid), 1200 mg of eqiv. Vitis vinifera extract and 2150 mcg of equiv. zinc
You may be able to help your body produce this important protein by making sure you get plenty of the following nutrients:
Vitamin C: Large amounts are found in blackcurrants, citrus fruits, berries, kiwifruit, tomatoes, broccoli, sprouts, capsicums
Proline: Large amounts are found in egg whites, beef, chicken, pork trotters, fish (cod and monkfish), wheat germ, dairy products, cabbage, asparagus and mushrooms (3).
Glycine: Large amounts are found in pork skin, chicken skin and gelatin, but Glycine is also found in high-protein foods meat, fish, dairy products and legumes
Copper: Large amounts are found in organ meats (liver), oysters, shiitake mushrooms, lobsters, leafy greens, sesame seeds, cocoa powder, cashews, lentils dark chocolate.
Additionally, your body needs high-quality protein that contains the amino acids needed to make new proteins. Meat, poultry, seafood, dairy, legumes and tofu are all excellent sources of amino acids.
Every Sunbio Collagen Peptides sachet contains a minimum of 4 grams of Premium quality Australian derived Collage Peptides per sachet. Collage Peptides contain eight (Methionine, Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Phenylalanine, Valine) of the 9 essential amino acids.
Benefits of Collagen Supplements
Two types supplements are gaining popularity: collagen peptides (collagen hydrolysate) and gelatin. Gelatin is created when collagen is cooked.
These have already broken the large protein down into smaller peptides, which are more easily absorbed in the body.
Below are some studies showing the benefits of collagen peptides for the following areas:
Muscle mass: In 2015 a scientific study in elderly men showed that a combination of collagen peptide supplements and strength training increased muscle mass and strength more than a placebo6.
Arthritis: Another scientific study gave supplements to people suffering from osteoarthritis. The participants who took collagen peptides experienced a significant decline in pain over the 70-day study, compared to those who took a placebo7.
Skin elasticity: A scientific study in 2014 found that women who took a collagen peptide supplement showed improvements in skin elasticity. Collagen is also used in topical treatments to improve the appearance of skin by minimizing lines and wrinkles8, 9.
Scientific Evidence
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21582/
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1606623/
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20620757
4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11966688
5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4665475/
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26353786
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22486722
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23949208
9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2923951/
上一篇:Is Collagen peptides a Miracle Cure?
下一篇:没有了!

 中文
中文